Kosher Gelatin: Functional & Nutraceutical Properties
Gelatin is a hydrocolloid; a protein or polysaccharide that, when mixed with water, provides textural effects such as thickening and gelling. Gelatin's unique amino acid composition and structure provide a range functional properties. Remarkable functionality combined with bland taste, color, and aroma make Geliko kosher gelatin an ideal choice for texturizing an array of kosher food, cosmetic, and pharmaceutical applications.
Gel Formation
Geliko kosher gelatin forms gels that are thermoreversible. Hot solutions as low as 0.5% gelatin will solidify when cooled, and revert back to a viscous solution if heated again. This transition can be performed repeatedly.
The relative gel strength of a gelatin product is indicated by its "Bloom" value, a measure of resistance to compression of a 6.67% gel prepared and held under prescribed conditions. Higher Bloom gelatins form stronger gels than lower Bloom gelatins (at the same concentration).
Gel strength is also affected by concentration, conditions of preparation such as temperature, pH, solids, etc., and the presence of other hydrocolloids such as agar, pectin, or carrageenan.
The following graph illustrates how gel strength varies with Bloom number.
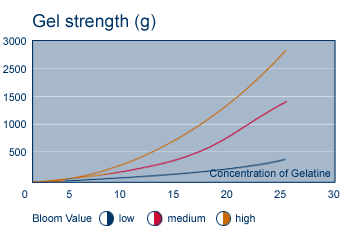
In addition to increased gelling capacity, gelatins with higher Bloom strength will exhibit the following characteristics:
·Solidification temperature is an important consideration when incorporating kosher gelatin into systems that require rapid gel formation (quick-set gummy candies, for example)
·Melting temperature will affect the mouthfeel of the finished product, allowing developers to create textures ranging from strong and chewy, soft and creamy
·Reduced usage level (to obtain the same gel strength as with a lower Bloom gelatin)
·Lighter color/increased transparency
·More neutral taste and aroma
·Thickening
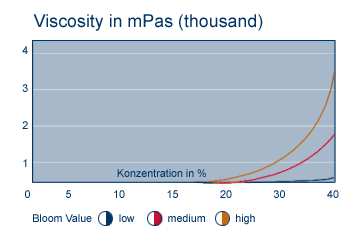
Aeration
Geliko kosher gelatin and kosher gelatin hydrolysates can be used to create foams. By decreasing surface tension, gelatin stabilizes aerated systems. (Surface tension effects also serve to stabilize emulsions such as those used for vitamin embedding.)
Film formation gelatin is able to stabilize surface interfaces by forming a film. This is an important function if disperse phases are to be protected within a particular medium. These effects are fully utilized in the production and stabilization of foams and emulsions. The surface tension of aqueous systems can be reduced by using gelatin.
Effect of pH on gelatin
The manufacturing process of gelatin determines its isoelectrical point (IEP), the pH at which the charge on the gelatin molecule is zero. The IEP of acid (Type B) processed gelatin such as Geliko kosher gelatin is between pH= 8.0 to 9.0.
At the isoelectric point, gelatin swelling, viscosity, and gelation are minimized, while gel strength, syneresis, turbidity, and foaming are maximized. Finished product pH is, therefore, a crucial factor to consider when selecting a gelatin product.
Nutraceutical properties of gelatin
Geliko kosher gelatin hydrolysates are a rich source of health-enhancing amino acids that enhance virtually any nutritional food, beverage, health and beauty aid, or pharmaceutical application. Gelatin hydrolysate contains high levels of arginine, essential for muscle cell metabolism, and glutamine, shown to reduce the effects of metabolic stress.
In a comprehensive range of clinical studies, it has been shown that gelatin hydrolysate can help maintain healthy joints, ligaments, and tendons.
Gelatin hydrolysate is also used in beauty products designed to enhance hair and nail growth, and promote healthy skin.
| Main Menu |
|---|
